Now Reading: Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Myths, and Dermatologist-Approved Treatments
-
01
Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Myths, and Dermatologist-Approved Treatments
Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Myths, and Dermatologist-Approved Treatments

Introduction
Hair loss in women is often dismissed as a rare or unimportant concern, but the reality is that over 50% of women experience noticeable hair thinning by age 50. Despite its prevalence, myths and misinformation abound, making it difficult for women to find effective solutions. In this expert-backed guide, we’ll break down the real causes of hair loss, debunk common myths, and explore science-backed treatments to help you regain fuller, healthier hair.
Understanding Female Hair Loss: Why It Happens
Hair loss in women is different from male-pattern baldness. Instead of a receding hairline or bald spots, women typically experience diffuse thinning, which makes the hair look less dense overall. Here are the main culprits:
1. Hormonal Imbalances & Androgenetic Alopecia (Female Pattern Hair Loss)
- The most common form of hair loss in women, female pattern hair loss (FPHL), is caused by sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone.
- DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink (miniaturization) and shortening the anagen (growth) phase.
- Often hereditary, but hormonal shifts like perimenopause and menopause can accelerate it.
2. Postpartum Hair Loss & Hormonal Fluctuations
- Estrogen levels skyrocket during pregnancy, keeping hair in the anagen (growth) phase longer.
- After birth, estrogen levels drop, causing a sudden shedding phase (telogen effluvium).
- This is temporary, but recovery can take 6-12 months.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
- Iron deficiency (anemia): Low ferritin levels affect hair follicle growth.
- Vitamin D deficiency: Linked to alopecia areata and weak follicles.
- Protein & biotin deficiency: Since hair is made of keratin (a protein), inadequate protein intake can slow growth.
4. Chronic Stress & Cortisol Dysregulation
- Stress triggers telogen effluvium, forcing too many hairs into the resting/shedding phase prematurely.
- Elevated cortisol levels also increase inflammation, disrupting healthy hair growth.
5. Thyroid Disorders (Hypothyroidism & Hyperthyroidism)
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism): Leads to dry, brittle hair and thinning.
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism): Can cause rapid shedding and hair fragility.
- Hair loss often reverses with proper thyroid treatment.
6. Scalp Conditions & Inflammation
- Seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff), psoriasis, and fungal infections can clog follicles, impairing growth.
- Excess oil, bacteria, and buildup suffocate follicles, triggering shedding.
Myths About Female Hair Loss
❌ Myth #1: Only Men Lose Hair Due to DHT
✔ Truth: Women also produce testosterone and DHT, making them susceptible to androgenetic alopecia.
❌ Myth #2: Washing Your Hair Too Often Causes Hair Loss
✔ Truth: Frequent washing doesn’t cause hair loss—but using harsh sulfates can weaken strands.
❌ Myth #3: Cutting Your Hair Makes It Grow Faster
✔ Truth: Hair grows from the follicle, not the ends—trims help prevent breakage, not speed up growth.
❌ Myth #4: Natural Oils Like Castor Oil Will Regrow Hair
✔ Truth: Oils can moisturize the scalp but won’t regrow hair affected by DHT or hormonal loss.
Dermatologist-Approved Hair Loss Treatments
1. Minoxidil (Rogaine) – FDA-Approved & Clinically Proven
- Increases blood flow to hair follicles, extending the anagen phase.
- Works for androgenetic alopecia & telogen effluvium.
- Results: 3-6 months for visible regrowth.
2. DHT Blockers: Finasteride & Natural Alternatives
- Finasteride (not typically prescribed for women pre-menopause) blocks DHT at the follicle level.
- Natural DHT blockers:
- Saw palmetto: Reduces DHT conversion.
- Pumpkin seed oil: Supports follicle health.
- Green tea extract: Contains anti-androgen properties.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- PRP injections use growth factors from your own blood to stimulate hair regrowth.
- Effective for: Androgenetic alopecia & thinning hair.
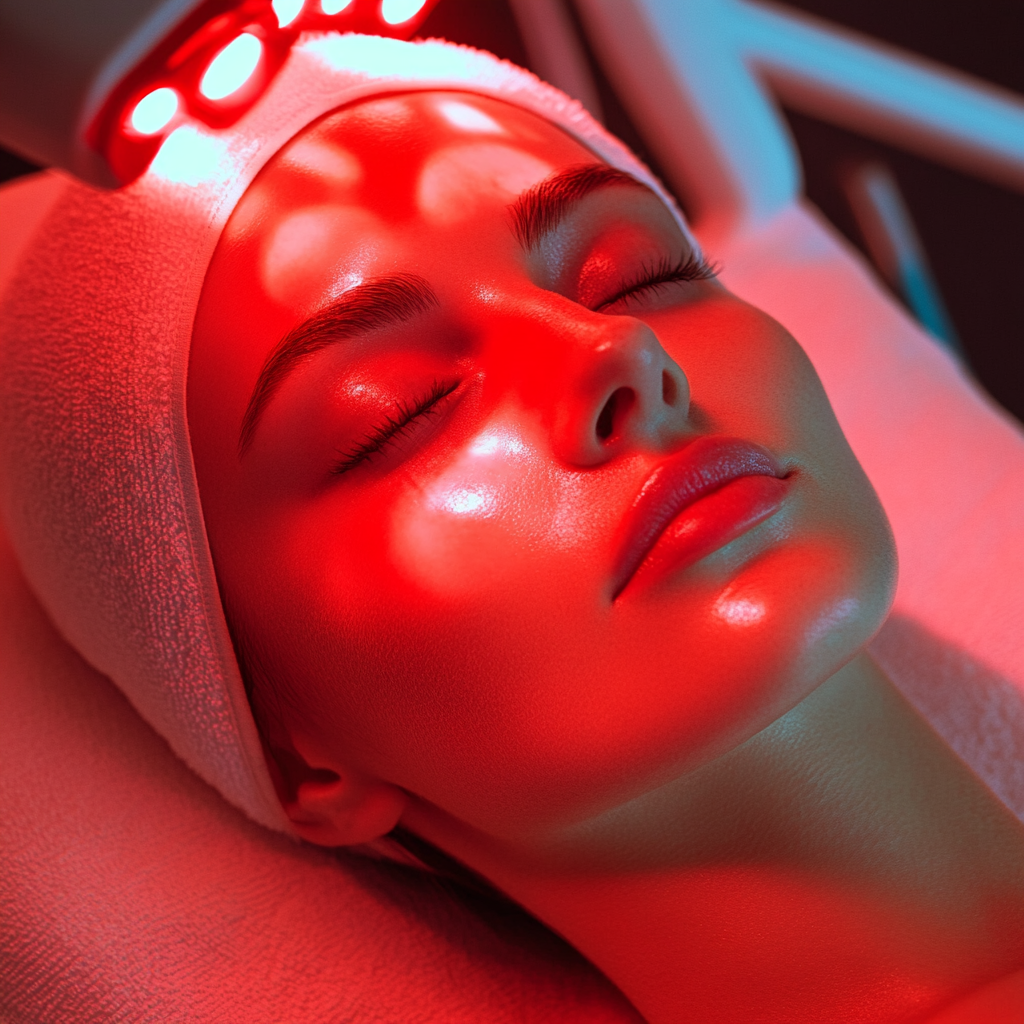
4. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Red light therapy boosts follicle energy production, helping to revive weak hair.
- Studies show LLLT increases hair density & thickness.
5. Scalp Microneedling
- Tiny micro-injuries trigger collagen production & enhance Minoxidil absorption.
- Works best for mild to moderate hair loss.
6. Hair-Friendly Nutrition
- Iron & Ferritin: Essential for oxygen delivery to follicles.
- Vitamin D: Regulates follicle cycling.
- Protein: Builds keratin, the protein structure of hair.
- Collagen & Biotin: Supports elasticity & thickness.
7. Stress Management & Lifestyle Tweaks
- Meditation, breathwork, & exercise can reduce cortisol levels.
- Good sleep hygiene supports hormone balance for optimal hair health.
What’s the Best Treatment for You?
The best approach depends on your specific type of hair loss:
| Cause | Best Treatment |
|---|---|
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Minoxidil, DHT blockers, PRP |
| Postpartum Hair Loss | Nutrition, scalp massage, time, Minoxidil |
| Telogen Effluvium | Stress management, iron, biotin |
| Thyroid-Related | Thyroid medication, iron |
| Scalp Conditions | Dandruff treatments, scalp exfoliation |
Final Thoughts: Regaining Your Hair & Confidence
Female hair loss is treatable—but early intervention is key. Whether you opt for FDA-approved treatments, holistic scalp care, or nutritional support, science-backed strategies can make a visible difference.
If you’re experiencing persistent hair loss, consult a trichologist or dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan.